Chapter 6
INPUT
1.1 What is Input?
Everything which given to computer is input. Somewhat data or facts that is directed to a computer meant for processing is measured as input.
1.2 Input Devices
The gadgets that are utilized to enter data and commands into a computer are entitled “input devices”.
The subsequent are Input Devices:
- Mouse
- Keyboard
- Microphone
- Webcam
- Joy Stick
- Light pen
1.3 THE KEYBOARD
A PC keyboard console is an input gadget that permits an individual to enter letters, numbers, and different images into a PC. It is perhaps the most utilized info gadgets for PCs. It is a bunch of keys that empower you to enter information into PC. A console contains numerous mechanical switches or press catches called keys.
There are major kinds of keys:
Numeric keys
Typewriter keys
Cursor control key
Function keys
i. Keyboard Ergonomics
An ergonomics is a PC keyboard console construct with ergonomics contemplations to limit muscle strain and a large group of related issues.
ii. Keyboards for Mobile Computers and Mobile Devices
A cellular phone is a general term for a handheld PC. These gadgets are intended to be amazingly versatile, and they can frequently fit in your grasp. Some cell phones like tablets, and cell phones are sufficiently incredible to do a considerable lot of very similar things you can do with a work area or PCs.
4. POINTING DEVICES
The devices that are used to move the cursor on screen is called pointing device.
The subsequent are pointing devices:
Mouse.
Trackball.
Joystick.
Pointing stick.
Wii Remote.
Finger tracking.
Graphics tablet.
Stylus
5. MOUSE
The mouse the is the pointer device which keep track the movement of cursor on pc screen. Mouse is a little hand-held pointing gadget which is gotten across a level surface or tangle to move a cursor on the PC screen. Mouse is also called a pointer. Mouse is a hand-worked input gadget used to control objects on the PC screen.
6. OTHER POINTING DEVICES
Additional pointing devices are defined below:
- Trackball
- Touchpad
- Pointing stick
Trackball
A trackball is a pointing gadget that is utilized to enter information into the PC or other electronic gadgets. Trackball compensates for PCs by and large fill-in as mouse reinforcement and principally used to move the cursor on the screen. A trackball requires remote arm and wrist movement that a customary mouse takes and consequently is regularly less unpleasant for the client to utilize.
Touchpad
A touchpad is a pointing gadget including a material sensor a specific surface that can interpret the movement and position of a client fingers to a general situation on the working framework. Touchpad has a vertical area for scrolling to work in any direction.
Pointing Stick
Pointing stick are used to manipulate the computer cursor like a joystick. If a laptop does not have sufficient space of a touchpad then pointing stick is a useful replacement.
7. TOUCH SCREENS AND TOUCH-SENSITIVE PADS
Touch screen is a touch presentation gadget. Touch screens that recognize numerous purposes of setting around then known as multi-contact. Since touchscreens need a great deal of arm and hand development, you don’t enter huge measure of information utilizing contact screen. All things considered, clients contact words, pictures, numbers, area, or letters recognized on the screen. i. Touch-Sensitive Pads
8. PEN INPUT
Pen input refers to the manner in which interrelating associate straightforwardly with a PC utilizing a pen. A pen can be utilized for pointing and furthermore for, straightforward content passage, and catching freestyle contemplations in advanced ink. The pen utilized for input has a fine, smooth tip that underpins exact pointing, composing or attracting ink.
9. OTHER INPUT FOR SMART PHONES
Other input approaches for cell phones just like Swipe and Swift key, offer considerable advantages to users and are comparable with mutual typing speeds originate on computer keyboards, according to a report published by researchers at Southborough University. Writing in a forthcoming issue of the Journal of Design Research, Tom Page, a lecturer in electronic product design, has assessed a number of different text input technologies available to smart phone users.
10. GAME CONTROLLERS
A game controller used to control coordinates the developments and activities of an objects in computer games. These devices have buttons and mini pointing devices that provide input to the computer such as:
- Gamepad
- Joystick and wheels
- Light guns
- Dance pads
- Motion-sensing game controllers
- Other game controllers
i. Gamepads
Gamepad controls the development and activities of a player or items in games. This gadget that incorporates programmable keys, directional and thumb stick. The client can utilize these capacities to play out specific activities, for example, changing a weapon, opening an entryway and so forth.
i. Joysticks and Wheels
A joystick comprises of a base and a stick. The stick can be moved toward any path to move an item around the PC. A joystick can perform comparable capacities to a mouse or potentially a trackball. The most recent joysticks, for example, Logitech G X56 are remote and costly. A Gaming wheel is an information gadget that utilizes a controlling haggle separate arrangement of pedals to reenact certifiable driving.
i. Light Guns
A light gun is a pointing input gadget that recognizes light utilizing a photodiode in the weapon barrel. At the point when the player pulls the trigger on the firearm, the screen is blanked for a small amount of a second. This concise second permits the photodiode to figure out where the weapon is pointed.
i. Dance Pads
Dance Pads is a level electronic game regulator utilized for contribution to move games.
Motion-Sensing Game Controllers
Movement sensing detecting game regulators permit the client to manage on-screen components or trigger occasions by moving a handheld information gadget in foreordained ways through the air. These regulators speak with a game comfort or PC through wired or remote innovation. An assortment of games from sports to reproductions use movement detecting.
Other Game Controllers
Most popular game controllers now-a-days are: Steel Series Stratus Bluetooth Game Controller Valve Steam Controller Logitech F710 Microsoft Xbox One Controller Xbox One Elite Wireless Controller
DIGITAL CAMERAS
Digital camera is a camera that catches photos in computerized memory. Be that as it may, film cameras can show pictures on a screen following being recorded and store and erase pictures from memory.
1.11.1 Digital Camera Photo Quality
A digital image is one of several factors that determine excellence of digital photo. The excellence of recording device. The size of digital image (pixels).
1.12 Video Input
input devices are as follow:
i. Web Cams
Webcam are commonly little cameras that either connect to a client screen. Most webcam interface with PC by means of USB, through exactly a Fire wire association.
1.12.2 Video Conferencing
A conference between two or more persons and different site by using a computer network to transmit audio and video data.
Example
- Video Telephone
1. SCANNERS AND READING DEVICES
A gadget that performs optical character acknowledgment and produces coded signals comparing to the characters recognized. PC input gadget that utilizes a light bar to examine codes, text, or realistic pictures straightforwardly into a PC or PC framework.
i. Optical Readers
An optical reader is a gadget found inside most PC scanners that catches visual data and makes an interpretation of the picture into computerized data the PC is equipped for comprehension and showing.
ii. Bar Code Readers
Bar Code Readers are electronic gadgets for perusing printed standardized tags. Bar Code Readers comprises of a light source, a focal point and a light sensor that makes an interpretation of optical driving forces into electrical ones.
i. RFID Readers
A radio frequency identification reader( RFID reader) is a gadget used to assemble data from a RFID tag, which is utilized to follow singular articles. Radio waves are utilized to move information from the tag to a reader.
Magnetic Stripe Card Reader
Magnetic Stripe Card Reader is an equipment gadget that peruses the data encoded in the attractive stripe situated on the rear of a plastic identification.
MICR Readers
The shortened form MICR represents Magnetic ink character acknowledgment. This is a kind of information input regularly found in banks. MICR innovation is utilized by banks. Numbers and characters found on the lower part of checks are printed utilizing attractive ink.
Data Collection Devices
Data Collection Devices/gadgets are characterized as the gadgets which help in getting information straightforwardly from the area where occasion or exchange happens.
1. BIOMETRIC INPUT
Biometric is use to innovation to confirm the personality of a person by checking individual qualities. Biometric gadget breaks down some biometric identifier and afterward award admittance to a program, framework or room. A biometric identifier is a physiological or social trait of an individual identified with the physical or compound exercises in the body. Some illustration of biometric identifiers f Optical Scanners.
OUTPUT
1) What is OUTPUT?
Output is a device used to send data from computer to another device and user. Most computer data output is meant for human, in the form of audio, videos. Output device is a peripheral that receive data from a computer. Computers can still working without output devices. So, there is no way to determine that what the computer doing. The key distinction between an input device and an output device is that an input device sends data to the computer, whereas an output device receives data from the computer.
Example
The most commonly used output devices are the following:
• Monitor
• Printer
• Audio Speakers
• Headphones
• Projector
• GPS
• Sound Card
• Video Card
• Braille Reader
• Plotter

2) Display devices
We can interact with the computer system through the Display Devices. The display devices enable us to communicate with the computer through the graphical interface.
Types
There are different types of Display Devices which are used to interact with the computer system or any other device. Some of them are following:
i. LCD Monitors and LCD Screens
A flat panel screen that use the liquid crystal display (LCD) technology and connects to a computer. Laptops have used LCD screens almost exclusively, and the LCD monitor is the standard display screen for desktop computers. This technology has replaced the traditional cathode ray tube (CRT) monitors, where the previous standard and where consider to have a better quality than LCD variants. LCD consumes less power than LED because they work on the principle of blocking light rather than emitting it.

ii. LCD Technology
LCD technology work by blocking lights. LCD is made of two pieces of substrate. Backlight creates light that passes through the first substrate. At the same time electric current allow light to pass through the second substrate and then create the colors and image that you can see on the screen
Types
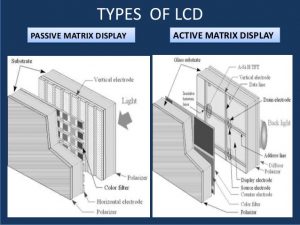
There are two types of LCD technology
i. Active matrix technology
LCD mostly used active matrix technology. A thin film transistor (TFT) arranges a capacitor in a matrix of the display. Addressed a particular pixel, the proper row switch on, then a charge is set down the correct column. All the other rows that the column intersect and turn off, only the capacitor receive a charge. Capacitor is able to hold the charge until the next cycle refresh.
ii. Passive matrix
LCD used to display a grid of conductive metal charge to each pixel. They are less expensive. Passive matrix monitors are rarely used today due to the technology slow response time and voltage are controlled compared to active matrix technology.
iii. LCD Quality
Quality is doing the right things right and is uniquely defined by each individual. A product or process that is Reliable, and that performs its intended function is said to be a quality product. To the degree which something meets or exceeds the expectations of its consumers. LCD screens come in various sizes and resolutions. Resolution is defined as the number of pixels or small dots that make up an LCD screen. The pixel is the smallest unit that makes up an image. Mostly TFT active matrix LCD screens are used. TFT active matrix is a technology in which each pixel has a transistor attached to control the backlight shining. Each pixel is made up of 3 sub-pixels (red, green and blue) all pixel having its own transistor. Each of these pixels turns on and off and filters light through colored sub-pixels which results in an image. Dot pitch is also called pixel pitch. Its distance between the pixels on the display device is millimeter. When text is created with a small dots pixel easily read it. Response time of the LCD screen it time is millisecond. That it take to turn a pixel on or off. LCD response times range 3to16 millisecond.
iv. Graphics, chips, ports and LCD monitors
I. Graphics
Cable on a monitor plugs in a port of the system unit. Chip is enable communication from a graphic chip. This chip is also called (GPU), control the manipulation and display graphic on the display devices
A digital image is a numeric representation of an image stored on a computer. They don’t have any physical size until they are displayed on a screen or printed on paper. Until that point, they are just a collection of numbers on the computer’s hard drive that describe the individual elements of a picture and how they are arranged. Some computers come with built-in graphics capability. Others need a device, called a graphics card or graphics adapter board that has to be added. Unless a computer has graphics capability built into the motherboard, that translation takes place on the graphics card. Depending on whether the image resolution is fixed, it may be of vector or raster type. Without qualifications, the term “digital image” usually refers to raster images also called bitmap images. Raster images are composed of pixels and suited for photo-realistic images. Vector image are composed of lines and co-ordinates rather than dots and is more suited to line art, graphs or fonts. To make a 3-D image, the graphics card first creates a wire frame out of straight lines. It also adds lighting, texture and color.
II. Chips
Computer chips, also called chip, integrated circuit or small wafer of semiconductor material embedded with integrated circuitry.
III. Ports
A computer port is a connection point or interface between a computer and an external or internal device. Internal ports may connect such devices as hard drives and CD ROM or DVD drives; external ports may connect modems, printers, mice and other devices.
IV. LCD Monitors
A flat panel screen that use the liquid crystal display (LCD) technology and connects to a computer. Laptops have used LCD screens almost exclusively, and the LCD monitor is the standard display screen for desktop computers.This is the most common computer output device. It creates a visual display by the use of which users can view processed data. Monitors come in various sizes and resolutions.
Types
Common Types of Monitors
• Cathode Ray Tube this uses phosphorescent dots to generate the pixels that constitute displayed images.
• Flat Panel Screen – this makes use of liquid crystals or plasma to produce output. Light is passed through the liquid crystals in order to generate pixels.
v. Plasma Monitors
A plasma display is a computer video display in which each pixel on the screen is illuminated by a tiny bit of plasma or charged gas, somewhat like a tiny neon light. Plasma displays are thinner than cathode ray tube (CRT) displays and brighter than liquid crystal displays (LCD). A plasma screen is made up of tiny cells containing noble gases and a tiny amount of mercury. These cells are in two pieces of glass and electricity is passed through the cells, causing the gases to turn into plasma. Light is then emitted, generating a picture on the screen. Plasma screens support high resolutions of up to 1920 x 1080.

vi. Television
Electronic system of transmit images of moving objects together with sound. A wire or through space by apparatus that converts light and sound into electrical waves and reconverts them into visible light rays and audible sound.

vii. CRT Monitor
CRT monitor is the most common type of display screen. It looks like a television. It can display graphics and text.
Working of CRT monitors
It uses a Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) to display an image on the screen. CRT consists of one or more guns that fire a beam of electrons inside the screen.CRT in color monitors consists of three guns. These guns generate red, blue and green.

3) Printers
i. Producing printed output
Data generated by a computer is referred as output. This includes data produced as a software level, such as the result of a calculation or at a physical level, such as a printed document. A basic example of software output is a calculator program that produces the result of a mathematical operation.
ii. Non-impact printers
A non-impact printer prints characters and graphics on paper without striking paper. Some printers use spray ink while other use heat and pressure to create images. These printers are faster than impact printer. However, they are more costly than impact printers. They produce no noise during printing. The print quality of non-impact printers is better than impact printers.

iii. Ink-jet printers
An ink-jet printer is a type of non-impact printer. It prints characters and graphics by spraying tiny drops of liquid ink on paper. These printers can produce quality text and graphics in both black-and-white and color including photos. A typical inkjet printer provides resolution of 300 dots per inch. The latest inkjet printers provide higher resolution. The price of inkjet printers is less than laser printers. However, they are slower than laser printers. Most inkjet printers can print from 10 to 35 pages per minute. Most inkjet printers usually have two print cartridges. One cartridge contains black ink and other contains color.

iv. Photo printer
Photo printer is a color printer that is specially designed to print high-quality photograph. It is also called snapshot printer. Some photo printer print photos of one or two sizes only.
v. Laser printer
LASER stands for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. The laser printer is a non-impact printer. Its working is similar to photocopying machine.it uses laser beams to burn special powder on page to create a permanent image. The power is contained in toner. Laser printer prints text and graphics in a high quality resolution. A typical laser printer provides the resolution of 1200dpi or more. Laser printer is mostly used in business field.

vi. Multifunction peripherals
A multifunction peripheral (MFP) is a device made up of multiple peripheral functionalities, capabilities including printing, copying, scanning. MFP performs a variety of function that would otherwise carry out by separate peripheral device. The printing device is mostly used in office. It is referred by printer, photocopier, scanning into a single device. Some are also used for emailing and faxing.
Benefits
• They reduce costs
• Low space requirement
• Provide a more particular solution that having many separate machines to complete the same task
Function
Printer perform many functions
• Envelope printing
• Collating, finishing functions
• Different paper formats, and high resolution printing for marketing materials.
• Some models also print directly from USB and other files, eliminating the need to boot up a computer for print quick print job.
MFP often has extensive capability, allowing them to deal with large volume of printing and very high quality printing for marketing material, including a variety of different paper sizes and types.
vii. Thermal Printers
Thermal printer is a printer in which fine heated pins form characters on heat sensitive paper. The thermal head generate heat; Rubber roller that feeds the paper; spring applies pressure on thermal head. A quality of print, speed it has become increasingly popular.
Working of thermal printer
It is used for heated pins and ribbons with different color bands. These printers contain a stick wax like ink. The ribbon passes in front of the head that has heated pins. These pins cause the wax to melt and when temperature reaches to certain level it is hardened
Uses
It is mostly used in airlines, banking, entertainment, retail, grocery and health care industries.
Advantages
1) Easier to use as there are less buttons and use of software involved
2) Popular in noise free environments and are great for offices.
3) Largely inexpensive and come in various models and sizes
4) Most efficient and faster in printing monochromic ones compared to other forms of printing
5) More durable compared to other printers.
DISADVANTAGES
1) Unlike standard printers, thermal printers usually do not print out colors well
2) If they become too heated to operate, the ink consumed would be more and the printing may not be precise
3) Print head could be harmed by the high heat used while printing, often resulting on cost to repair when it break down.

viii. Mobile printers
Mobile printing is the process of sending data to a printer wirelessly from a smartphone or tablet. One involves direct communication between a mobile device and a printer. The other approach involves communication between a mobile device and a computer connected to a printer.
Benefits of mobile printers
• Enhanced productivity
• Better customer services
• Potential for cost saving
• Enhanced flexibility
ix. Label and postage printers
A label printer is a computer printer that prints on self-adhesive label material and card-stock (tags). A label printer with built-in keyboard and display for stand-alone use (not connected to a separate computer) is often called a label maker.
Types of label printers
• Desktop label computers
• Commercial label printer
• Industrial label printer
x. Plotter and large format printers
• Plotters
A plotter is an output device that is used to produce high quality graphics in a variety of colors. Plotters are used to create architectural design, graphs, maps and charts.
Types of plotters
Different types of plotters are as follows:
I. Flatted plotter
II. Drum plotter
• Large format printers
Large Format Printing refers to print materials that are too large to be printed on the most readily available sizes of commercial printing presses. In the print industry, “large format” is actually a relative term because maximum print sizes vary from printer to printer.
xi. Impact printers
An impact printer works like a typewriter.it prints characters or image by striking a print hammer. Impact printers are the oldest print technologies which are still produced. The impact printers are used where low-cost printing is required.
Three most common forms of impact printers are as follows:
1. Dot matrix printers
2. Daisy wheel printers
3. Line printers
4. Speakers, Headphones and Ear buds
Speakers
Speakers are one of the most common output devices used with computer systems. Speakers are transducers that convert electromagnetic waves into sound waves. The speakers receive audio input from a device such as a computer or an audio receiver.
Headphones
Headphones are a pair of small speakers used for listening to sound from a computer, music player or other such electronic device. Headphones originally consisted of one speaker for each ear, connected by a band over the head.
Ear buds
Smaller headphones, often called ear buds or earphones, are placed inside the outer part of your ear canal. Like speakers, headphones contain transducers that convert an audio signal into sound waves.
a. Data projectors
A device that projects computer output onto a white or silver fabric screen that is wall, ceiling or tripod mounted. It is widely used in classrooms and auditoriums for instruction and slide presentations. For projectors designed primarily to display movies, see front-projection TV. A data projector is a projection device that takes a signal output by a computer and projects an image onto a projector screen via a lens system. Data projectors can be used in such applications as home theater, conference room presentations and classroom training. A data project is used to project the contents of a computer screen onto a big screen or wall so that a large audience can see the information. Data projectors are particularly popular for use with presentation software.
Display Resolution
Display resolutions, or the number of pixels displayed in an image, for a data projector range from 1280×720 pixels to 1920×1080 pixels. Extended graphics array (XGA) projectors offer standard resolutions of 1024×768 pixels, while super video graphics array (SVGA) projectors include resolutions of 800×600 pixels.
Types
Cathode ray tube (CRT) data projectors project light through red, green and blue colored tubes, and are heavier and larger than many other data projector systems. Liquid crystal display (LCD) data projectors utilize a lamp and prism system to project signals and are typically used for business and home theater purposes.
Function
A data projector is used with either laptop or desktop computers. Projectors use S-Video, RCA cables or USB connections to hook to the computer. In classrooms and business presentation rooms, data projectors are often hooked to both computer and video equipment.
Uses
The most ubiquitous use of a data projector is for presentations in business meetings or classrooms. Presentation software allows a user to create slide shows of photos, type written information and display graphs. Teachers in high school and college make extensive use of data projectors to give notes or lectures, as do business people making presentations to co-workers or clients.
Advantages of data projector
Compared the previous projection technologies and other ways of presenting information, a data projector has several distinct advantages.
i. Flexibility
You can connect a data projector to any digital image output device, computer, and smartphones to share files on the screen with the audience. The connection to be rather simple and you can also adjust your projector setting and also you can change the size of screen according to the size of the audience. Data projector main high quality reliable
ii. Perfect companion
Data projector is a light weight device. It is design to transport easily and set in different location to making the perfect companion for global business where you have opportunity to present the audience
iii. Multimedia
Data project support multimedia like video that are connected to a sound system (audio). A multimedia used to keep your audience interested
iv. Online use
Data projector allows projecting your computer or mobile screen while you consult web resources.

b. Interactive whiteboard
An Interactive Whiteboard (IWB) is a large, touch‐sensitive (thus interactive) board that when used with a combination of a computer and digital projector facilitates interactive ICT engagement. It resembles a traditional whiteboard and can be used similarly. The computer connected to the interactive whiteboard can be controlled by touching the board directly or by using a special pen. From the research available, it seems clear that the interactive whiteboard is widely considered to be a positive and motivational asset to the classroom. An interactive whiteboard, also known as a smart board, is an interactive display in the format of a whiteboard that reacts to user input either directly or through other devices. Standard white boards have been most commonly used to share message, important information. The interactive white board has the ability to connect the internet. Interactive white board includes easy to use charts, graphs, tools might find in the classroom like ruler, compasses or protectors. They can provide various types of media and provide teachers for interactive lectures to the students
Advantages
Interactive whiteboard is an improvement in the education sector by simplifying the learning processes
• Review or revision
This is a main advantage of interactive whiteboard it allows to the student to save lesson for later review. It provides the opportunity to share text, video, audio files in the classroom. The recorded lesson is providing more convenient reference point during revision. This is help out the student to better understand, quicker learning and improved performance.
• IT is easier for teachers
Nowadays, teachers in learning institutions are using LCD monitors displays together with shared whiteboards to deliver lessons. Every student will be trying out how the board works. That can spur the students ‘enthusiasm to get involved in learning process using the interactive whiteboards. Images and presentations are delivered in full HD display accompanied by interactive computer capabilities. Students in such learning environment will find syllabus coverage more fun them and they can understand easily
• Flexibility in learning
The interactive whiteboard that is allow the teachers to share notes and other learning tools to the students. The use of the interactive whiteboard insures the learning needs of every student are fulfill.
• LEARN BETTER
Another benefit of the interactive whiteboard in the classroom is that help the student to hearing a benefit from visual presentation. They can also learn more about a topic using audience presentation
c. Force-feedback game controller and tactile output
Force-feedback game controller
Force-feedback is most commonly used technology to game controller. It is uses small motors built into the game controller it provide physical feedback under the control of game software designed to use force feedback.
For example
Force-feedback joystick, as you pull a 7G turn you feel the joystick jerk and jitter as the aircraft control surfaces lose laminar flow, but as you can extend to gain airspeed, the controls settle down again. When you come up on the six of a bandit and begin hosing him down with your 30mm rotary cannon, the joystick stutters as the gun recoils. Well-implemented force feedback greatly enhances the ambiance of games that support it properly, but the quality of force-feedback hardware varies great between controllers. Even more important, games in how well they integrate force feedback. Well-designed games use it to make the game more immersive. Force-feedback uses it in only the most basic ways. This problem seems to be disappearing as new releases of such games usually make better use of force feedback. The only real drawback to force feedback is that it is expensive. Force feedback isn’t very realistic. Force feedback is just a device to let you know what’s going on with the car, in real life you have not only the feel through the wheel but also the seat, pedals and the forces being put through your body.
Tactile output
Tactile output provides the user with the physical response from the device. Haptic technology or hap tics, is a tactile feedback technology which takes advantage of the sense of touch by applying forces, vibrations, or motions to the user. Several printers and wax jet printers have the capability of producing raised line drawings. There are also handheld devices that use an array of vibrating pins to present a tactile outline of the characters or text under the viewing window of the device. Haptic technology, or haptic, is a tactile feedback technology which takes advantage of the sense of touch by applying forces, vibrations, or motions to the user. Several printers and wax jet printers have the capability of producing raised line drawings.
OUTPUT
WHAT IS OUTPUT?
Data generated by a computer is referred to as output. This included data produced at a software level, such as the result sum of a calculation, or at a physical level, such as a printed document. A basic example of software output is a calculator program that produce the result of a mathematical operation. A more complex example is the results produced by a search engine, which compares keywords to millions of pages in its Web page indexing. An output device is any device that receives data from a computer, usually for display, projection, or physical reproduction. For example, the printer is an output device that can make a hard copy of anything shown on the monitor. Monitors and printers are two of the most commonly used output devices used with a computer.
What are the output devices of computer?
Every computer has a monitor, an audio adapter, and a GPU. Each of these is an output device. A printer is also very commonly used with computers. Depending on the type of computer and how the computer is used, other output devices may be used with a computer. The best method of determining all of the output devices your computer has is to go through the list above.
Why do computers need output devices?
A computer cannot still work without an output device. However, you’d have no way of determining what the computer is doing. By using an output device, you can view and get the results of input from a computer.
How does an output device work?
An output device works by receiving a signal from the computer and using that signal to perform a task to display the output. For example, below is a basic list of steps of how an output device works. On a computer keyboard (input)if you type “H”, it sends (input) a signal to the computer. The computer processes the input and once completed, sends a signal to a monitor (output device). The monitor receives the signal and displays (output) the “H” to the screen. If supported, that “H” could also be printed (outputs) to a printer, which is another example of an output device. If no output device was connected to the computer and it was functional, you could still type “H” on the keyboard, and it would still be processed. However, you’d be unable to see what happened or confirm the input with no output device. Computer output devices are all peripheral hardware devices, and are connected to a computer by cables, or by wireless networking.
Reasons for Having an Output Device
A computer can still function without an output device. However, without an output device, there’s no way to determined what the computer is doing. There is no indicator of errors, nor of the need for additional input. For example, if you detach your monitor from your computer, the computer will still function, but it’s not going to be very helpful.
Examples of Output Devices
Monitor
This is the most common computer output device. It creates a visual display by the use of which users can view processed data. Monitors come in various sizes and resolutions.
Common Types of Monitors
Cathode Ray Tube
This uses phosphorescent dots to generate the pixels that constitute displayed images.
Flat Panel Screen
This makes use of liquid crystals or plasma to produce output. Light is passed through the liquid crystals in order to generate pixels. All monitors depend on a video card, which is positioned either on the computer motherboard or in a special expansion slot. The video card sorts out the computer data into image details that the monitors can then show.
Printer
this device generates a hard copy version of processed data, like documents and photographs. The computer transmits the image data to the printer, which then physically recreates the image, typically on paper.
Types of Printers
Ink Jet
This kind of printer sprays tiny dots of ink onto a surface to form an image.
Laser
This type utilizes toner drums that roll through magnetized pigment, and then transfers the pigment onto a surface.
Dot Matrix
Dot matrix printers utilize a print head to set images on a surface, using an ink ribbon. These printers were commonly used between 1980 and
Speakers
Speakers are attached to computers to facilitate the output of sound; sound cards are required in the computer for speakers to function. The different kinds of speakers range from simple, two-speaker output devices right the way up to surround-sound multi-channel units.
Headset
This is a combination of speakers and microphone. It is mostly used by gamers, and is also a great tool for communicating with family and friends over the internet using some VOIP program or other.
Projector
This is a display device that projects a computer-created image onto another surface: usually some sort of whiteboard or wall. The computer transmits the image data to its video card, which then sends the video image to the projector. It is most often used for presentations, or for viewing videos.
Plotter
This generates a hard copy of a digitally depicted design. The design is sent to the plotter through a graphics card, and the design is formed by using a pen. It is generally used with engineering applications, and essentially draws a given image using a series of straight lines.
Input/output Devices
Input/output devices don’t only produce output, but can also be used as storage and input devices. The computer transmit data to the drive, where it is saved and can be later accessed. Examples of I/O devices are CD drives, DVD drives, USB drives, hard disk drives (HDDs), and floppy disk drives. CDs and DVDs are two kinds of optical disc which save data in a digital format. Data is written onto the disc using a laser writer that embeds the data directly into the disc’s coating. A floppy disk is a magnetic storage device. A layer of magnetized material is placed within a proactive plastic casing. The computer then embeds the data into the magnetized material, by using a writing head. Here is the different type of Output Devices
DISPLAY DEVICES
- LCD Monitors and LCD Screens
- LCD Technology
- LCD Quality
- Graphics Chips, Ports, and LCD Monitors
- Plasma Monitors
- Televisions
- CRT Monitors
Display Devices
A display device is an output device for presentation of information in visual or tactile form (the latter used for example in tactile electronic displays for blind people). When the input information that is supplied has an electrical signal the display is called an electronic display.
In use
These are the technologies used to create the various displays in use today.
- Electroluminescent (ELD) display
- Liquid crystal display(LCD)
- Light-emitting diode (LED) backlit LCD
- Light-emitting diode (LED) backlit LCD
- Thin-film transistor (TFT) LCD
- Light-emitting diode (LED) display
- OLED display
- AMOLED display
- Plasma (PDP) display
- Quantum dot (QLED) display
Uses
A display is a computer output surface and projecting mechanism that shows text and often graphic images to the computer user, using a cathode ray tube ( CRT ), liquid crystal display ( LCD ), light-emitting diode, gas plasma, or other image projection technology.
Advantages of display deceive
The main advantages of LCD’s over CRT displays are that LCD’s consume less power, take up much less space, and are considerably lighter. The now common active matrix TFT-LCD technology also has less flickering than CRTs, which reduces eye strain.
Disadvantages of display deceive
In case you are using your computer as a server and it’s providing some kind of service to the other computers on the network, let’s say your computer is acting as a file server where users on the network store their data. In this case rarely one needs to work physically on the sever, because all the users are accessing the services remotely, and connecting a display device such as a Monitor to a server can be security concern. Because it will be very hard for a not authorized person to do anything on the machine even if he gains physical access to a without a display device.
LCD Monitor
A liquid crystal display (LCD) monitor is a computer monitor or display that uses LCD technology to show clear images, and is found mostly in laptop computers and flat panel monitors. This technology has replaced the traditional cathode ray tube (CRT) monitors, which were the previous standard and once were considered to have better picture quality than early LCD variants. With the introduction of better LCD technology and its continuous improvement, LCD is now the clear leader over CRT, in terms of color and picture quality, not to mention capabilities for large resolutions. Also, LCD monitors may be made much more cheaply than CRT monitors.
LCD monitors
The LCD monitor incorporates one of the most advanced technologies available today. Typically, it consists of a layer of color or monochrome pixels arranged schematically between a couple of transparent electrodes and two polarizing filters. Optical effect is made possible by polarizing the light in varied amounts and making it pass through the liquid crystal layer. The two types of LCD technology available are the active matrix of TFT and a passive matrix technology. TFT generates better picture quality and is more secure and reliable. Passive matrix, on the other hand, has a slow response time and is slowly becoming outdated.
Various different LCD technologies are used today, including:
- In Plane Switching (IPS) Panel Technology: These panels are considered to have the best color accuracy, viewing angles and image quality in LCD technology.
- Super Plane to Line Switching (PLS): Developed by Samsung, this LCD panel is very similar to the IPS panel but reportedly, it is 10 percent brighter, has wider viewing angles and is cheaper to produce.
- Vertical Alignment (VA) Panel Technology: These panels are considered to be in the middle of TN and IPS technology. Compared to TN panels, they offer wider viewing angles and better color quality but have slower response times. They have higher contrast ratios, compared to the other panels but have a downside, in terms of color shifting, where the brightness display is unevenly distributed throughout the screen.
- Twisted Noematic (TN) Panel Technology: These panels are the most commonly used type of panel in LCD technology. They are cheaper and offer faster response times, making them a preferred choice for gamers. The downside is that the viewing angles, contrast ratios and color production are considered the lowest of LCD panel types.
Advantages of LAD MONITERS
The advantages of LCD monitors include their compact size which makes them lightweight. They also don’t consume much electricity as CRT monitors, and can be run off of batteries which makes them ideal for laptops. Images transmitted by these monitors don’t get geometrically distorted and have little flicker. Images transmitted by these monitors don’t get geometrically distorted and have little flicker. However, this type of monitor does have disadvantages, such as its relatively high price, an image quality which is not constant when viewed from different angles, and a monitor resolution that is not always constant, meaning any alterations can result in reduced performance.
LCD display technology.
LCD screens are an array of small segments called pixels, which can be manipulated for information displaying. Such displays have several layers, where two panels, made of glass material free of sodium and called substrate, play a crucial role. The substrate contains a thin layer of liquid crystals between them. The panels have flutes that direct the crystals, giving them a distinctive orientation. Flutes are parallel on each panel but are perpendicular between the two of them. Longitudinal flutes are obtained as a result of placing on the glass surface thin films of transparent plastic, which are then processed in a particular way. In contact with the flutes, the molecules are oriented identically in all the cells. The liquid crystal panel is illuminated by a light source, depending on where it is located, as the LCD panels operate on reflection or light transmission. The plane of polarization of the light beam is rotated by 90° as one panel passes. When an electric field appears, the molecules are partially aligned along it, and the angle of rotation of the plane of polarization of light becomes different from 90°. By producing screens using LCD monitor technology, the backlight of the monitor is used to output a color image so that light is generated at the back of the LCD monitors. It is necessary to be able to have a picture with good quality, even if it is dark. The color is obtained using three filters, which distinguish three principal components from the radiation of a white light source. By combining the three primary colors for each pixel of the screen, you can reproduce any color.
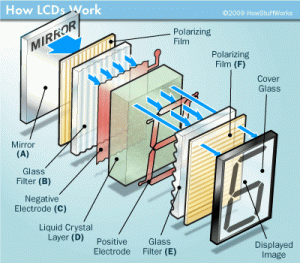
Modern LCD screens are also called flat panels, dual scan active matrix, and thin-film transistors. Now they are extremely popular – everyone likes their elegant look, thinness, compactness, and efficiency. LCD monitors provide a quality contrast, and bright, clear images. In the past, liquid crystal technology was slow, not as efficient as now, and their contrast level was low. The first matrix technologies, the so-called passive matrices, worked quite well with textual information, but with a sharp change in the picture, so-called “ghosts” appeared on the screen. Since LCD technology orients each pixel separately, the clarity of the received text is higher in comparison with CRT monitors, which in the past could compete with LCD ones. Now, of course, with the development of technology and taking into account the overall technological process, liquid crystal monitors have long been ahead and occupy a leading position among the displays used for various applications. Monitors based on liquid crystals are widely utilized not only in desktop computers but also in an array of electronic devices: TVs, photo and video cameras, laptops, tablets, smart-phones, car navigators, e-books, MP3 and other players, watches, etc.
LCD
LCD Stands for “Liquid crystal display.” LCD is a flat Panel display Technology commonly used in TV computer and monitors. It is also used in Screens for Mobiles and device, Such as laptops, tablets, smart-phones. liquid Crystal display technology works by blocking light. Specifically, it is made of two pieces of polarized glass that contain a liquid crystal material between them. A backlight creates light that passes through the first substrate.
Characteristic of LCD
Native Resolution. Unlike CRT monitors, LCD monitors display information well at only the resolution they are designed for, which is known as the native resolution. …
- Viewing Angle.
- Brightness or Luminance.
- Contrast Ratio.
- Response Rate.
- Adjustability.
Uses of LCD
LCD is used produce a visible image. Liquid crystal displays are super-thin technology display screen that are generally used in laptop computer screen, TV, cell phones and video games. LCD technologies allow displays to be much thinner when compared to cathode ray tube.
Advantages of LCD
- LCD consumes less amount of power.
- LCD is of low cost.
- LCD provides an excellent contrast.
- LCD is thinner and lighter.
- It produces very bright images.
- It is energy efficient.
- It takes up about 40% less desk space.
- It’s a completely flat screen.
- It gives good color reproduction.
Disadvantages of LCD
- The resolution is fixed.
- Producing deep black is very difficult.
- Pixels are dead
- color depth is fixed.
- The LCD display has slow response times.
- LCD cost is considerably at a high price.
- The native resolution cannot be changed.
- viewing angles affect the brightness.
Graphics Card Outputs
Modern desktop computers and notebooks comprise of a CPU, motherboard, graphics, storage, and, usually an optical drive. Computers have a number of ports and sockets that enable the user to plug-in various peripherals such as a printer, USB mouse, or, perhaps most importantly of all, an Internet connection. Looking at it from the other side, desktop computers need to be attached to a monitor or television so that one can view the output of the graphics – the text on the display, for example – and to this end have numerous graphics-related outputs. Notebooks have built-in screens so do not need these additional outputs unless transmitting to a larger screen. Desktop computers’ graphics stem from two sources. Firstly, the machine may have basic graphics capabilities that are integrated into the motherboard. These are called integrated graphics and are found on low-cost computers. More-expensive PCs have what are known discrete graphics, whereby a dedicated graphics card is placed into the system and used to run games at high-quality settings. Both sets of graphics can be outputted to a display in various ways. These include connections known as VGA, DVI, HDMI and Display-Port. This TekSpek looks at the common interfaces and explains how they work. A GeForce GTS 450 graphics card, released in September 2010, is shown with various outputs in the picture, below. This TekSpek will reference it during the discourse.

VGA
The oldest type of video connector still used on modern PCs is Video Graphics Array (VGA). It is the blue-colored port in the middle of the graphics card. First introduced in 1987 by IBM and also referred to as HD15 – representing the number of pins in the connector – the VGA video connection flourished for a good 15 years after its inception. Indeed, the very fact that it’s still specified on new graphics cards is a testament to its longevity. VGA is an analogue connection that is primarily used to connect the graphics card to older CRT monitors that process data in analogue form. This means the CRT receives electrical signals in a continuous form, rather than the pulsing found on newer digital displays. Because CRTs have been around for more than 30 years and still represent a reasonable proportion of displays used in businesses, graphics-card manufacturers have kept this legacy connector alive. The VGA connector requires the graphics card to convert its native digital output into analogue form before sending it out over the VGA cable and to the monitor. The quality of the digital-to-analogue convertor (DAC) largely dictates the quality of the picture on the CRT. VGA has a maximum supported resolution of 2,048×1,536 pixels, though it is usually limited to 1,600×1,200 on most monitors.
DVI
The emergence of flat-panel displays in the last 10 years has led to the decline of VGA and rise of Digital Video Interface (DVI) as the de facto display standard. Flat-panel screens – think of LCD monitors and TVs here – use a digital format for the display. This means that the graphics card can send its digital output to the display without the need to convert it into an analogue signal first. The white-colored DVI connector, shown on the right of the picture, is connected to what is known as a Transition Minimized Differential Signaling (TMDS) chip on the graphics card. The TMDS grabs the signal from the video card and then passes it over to the display, optimizing the resolution and refresh rate in the process. You will find a DVI connection on practically all graphics cards and flat-panel monitors nowadays. There are two forms of DVI connections for the consumer market. Most monitors have what is known as a single-link connection that uses a single TMDS to provide the output. The resolution of this link, for the most part, is limited to 1,920×1,200 pixels and is therefore fine for the majority of displays. High-resolution monitors – 30in models, in the main – have a 2,560×1,600px resolution and need two TMDS transmitters and a special cable for what is known as a dual-link connection. DVI is further split into DVI-I and DVI-D, where the former also supports an analogue connection by having four additional pins on the right-hand side of the port – as you can see on the pictured graphics card. DVI can also carry the optional High-Bandwidth Digital Content Protection (HDCP) feature that inhibits the copying of digital data by encrypting it before it’s sent over the cable to the monitor.
HDMI
Whereas DVI is aimed squarely at the PC market, High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) provides the same digital data transfer for consumer-electronic devices such as flat-panel TVs, modern consoles, DVD- and Blu-ray players, home-cinema equipment, and, increasingly, on graphics cards (the left-hand port in the picture). Both DVI and HDMI transmit uncompressed digital data from source to display, but HDMI’s one big advantage is that it can also send up to eight channels of compressed or uncompressed sound via the single cable. HDMI is electrically very similar to DVI, insofar as a basic DVI-to-HDMI adapter can be used without a loss of quality. HDMI, however, requires that HDCP encryption is mandatory. The digital connection has been updated numerous times since its launch in 2002. The latest version is HDMI 1.4, which supports advanced features such as an ultra-high-resolution of 4,096×2,160px, an Ethernet channel and 3D compatibility. The wide proliferation of HDMI in consumer-electronic devices means that it has now overtaken DVI as the digital connection of choice. From a computing perspective, AMD and NVIDIA’s newest graphics cards are able to take the audio from the computer and ferry it through the HDMI port to an HDMI-equipped monitor or TV with both the video and audio streams present. HDMI implementation currently costs four cents (US) per device and a $10,000 annual fee for manufacturers with a high volume of HDMI-equipped parts.
Display Port
The newest mass-market digital interface is known as DisplayPort. Released in 2007, it is designed to replace both DVI and VGA as a single-cable connection to computer monitors. The 20-pin connection isn’t directly compatible with DVI unless used in a dual-mode DisplayPort configuration, which itself is limited to single-link DVI transmissions. DisplayPort uses a system of what are termed differential data pairs within a main link to transmit data.

Up to four differential pairs are teamed up to provide the bandwidth, which can be used for both video and audio signaling. At its peak, a four-pair DisplayPort connection can transmit 17.28Gbit/s of data. It offers optional HDCP and advanced DisplayPort Content Protection, as well. Chip-maker AMD has already taken DisplayPort on-board with its Infinity multi-monitor feature, where up to six displays can be connected to a single graphics card for increased productivity and large-area gaming. Laptop-makers are also looking at DisplayPort to replace the many-wire LVDS system that currently connects the motherboard’s display electronics to the screen itself. Now gaining in momentum, Intel is providing DisplayPort as standard on its next-generation Sandy Bridge architecture.
Plasma Monitors
A plasma is a computer video display in which each pixel on the screen is illuminated by a tiny bit of plasma or charged gas, somewhat like a tiny neon light. Plasma displays are thinner than cathode ray tube displays and brighter than liquid crystal displays.
Plasma monitor work
When electricity flows into the tube, gas atoms crash about inside it and generate invisible ultraviolet light. The white phosphor coating turns this invisible light into visible white light. In a Plasma TV, the cells are a bit like tiny CFLs only coated with phosphors that are red, blue, or green.
Advantages of Plasma monitors
- Capable of producing deeper blacks allowing for a superior
- As they use the same or similar phosphors as are used in CRT displays, plasma’s color reproduction is very similar to that of CRTs.
- Wider viewing angles than those of LCD
- Superior uniformity. LCD panel backlights nearly always produce uneven brightness levels, although this is not always noticeable. High-end computer monitors have technologies to try to compensate for the uniformity problem.
- Unaffected by clouding from the polishing process. Some LCD panel types, like IPS, require a polishing process that can introduce a haze usually referred to as “clouding”.
- Less expensive for the buyer per square inch than LCD, particularly when equivalent performance is considered.
Disadvantages of Plasma monitors
- Does not work as well at high altitudes above 6,500 feet (2,000 meters)
- Plasma displays are generally heavier than LCD and may require more careful handling such as being kept upright.
Plasma Vs LED
Plasma vs Led, while an LED screen uses light-emitting diodes as backlights for the screen, plasma screens light themselves using gas cells that emit ultraviolet light. LED-blacklight screens are an improvement over regular LCD screen.
Television:
A system for converting visual images into electrical signals, transmitting them by radio or other means, and displaying them electronically on a screen. A television is a machine with a screen. Television receive broadcasting signals and change them into pictures and sound. The word “television” comes from the words tele (Greek for a faraway) and vision (sight). Computers and mobile devices also can used for watching television programs.

History:
The First Electronic Television was invented in 1927. The world’s first electronic television was created by a 21-year-old inventor named Philo Taylor Farnsworth. That inventor lived in a house without electricity until he was age 14.

Uses:
Television is a system for transmitting visual images and sound that are reproduced on screens, chiefly used to broadcast programs for entertainment, information, and education. The television set has become a commonplace in many households, businesses, and institutions.
Characteristics:
TV has both sound and sight. A TV broadcast is conceived and produced and received in audio-visual terms. As eyes absorbs and retain much more than the ear so, TV broadcasts have greater influence on viewers than radios audience.
Positive Effects:
- Educational
- Entertainment
- Sports
- Exposure to different cultures
- Television can inspire
- 3D TV and program
- Curbs Physical Activity
- Impact Social Development
Is TV a waste of time?
It’s pretty obvious that when you’re watching TV, you’re not doing anything else. Time spent watching television is similar to being asleep (although you will see some other consequence below).
Advantages:
- In this busy, expensive life, television is an easy and cheap source of entertainment.
- By watching international news, we are kept informed and up-to-date with breaking news around the world.
- Some shows and channels offer educational programs that can increase our knowledge and make us more aware of the world around us.
- Some shows can motivate people who are interested in that field and help them to pursue their dreams.
Disadvantages:
- Sex, Crime, and violence are frequently depicted on television and may have negative effects on impressionable children. Kids who see violent acts are more likely to display aggressive or violent behavior and also to believe that the world is a scary place and that something bad is going happen to them. Ongoing studies have shown a lasting correlation between watching violence on television and aggression that begins in childhood and continues into adulthood. Viewers sometimes imitate violent, criminal, sexual, or other risky behavior they see on television and end up in trouble, in jail, or in a hospital as a result.
CRT Monitor:
CRT may refer to any of the following:

1. Short for cathode ray tube, a CRT is the electron beams in a monitor that move across your screen either interlaced or non-interlaced, hitting phosphor dots on the inside glass tube. The picture is an example of the inside of a computer monitor that shows the CRT connected to the screen. In the CRT are three electron guns: red, green, and blue. Each of these guns streams a steady flow of electrons, left to right, for each line of your monitor. As the electrons hit the phosphors on the CRT, the phosphor will glow certain intensities. As a new line begins, the guns will then begin at the left and continue right. These guns will repeat this process sometimes thousands of times until the screen is completely drawn line by line. Once the phosphors on the CRT have been hit with an electron, they only glow for a short period of time. Because of this, the CRT must be refreshed, which means the process will be repeated as explained above. If the video card’s refresh rate is not set high enough, you may encounter a flicker or a noticeable steady line scrolling from the top to the bottom of your screen.
History of the CRT
While cathode rays were first discovered in 1869 by Johann Hittorf, it wasn’t until 1897 that the first CRT was invented by Ferdinand Braun. Named the “Braun tube,” the first CRT used a code-cathode diode, having a phosphor coated screen. John B. Johnson and Harry Weiner Weichert created the first CRT to use a hot cathode, turning it into a commercial product in 1922. In 1934, the first CRT televisions were made available commercially in Germany by Telefunken. Since then, CRT technology was improved many times and utilized in computer monitors, as well as televisions. CRT monitors and televisions were widely used around the world until the 2000s, when LCD technology became more popular and began to replace CRT. Today, CRT is considered mostly obsolete.
2. PRINTERS
i. Producing Printed Output
ii. Nonimpact Printers
iii. Ink-Jet Printers
iv. Photo Printers
v. Laser Printers
vi. Multifunction Peripherals
vii. Thermal Printers
viii. Mobile Printers
ix. Label and Postage Printers
x. Plotters and Large-Format Printers
xi. Impact Printers
Printer:
A printer is a device that accepts text and graphic output from a computer and transfers the information to paper, usually to standard size sheets of paper. Printers vary in size, speed, sophistication, and cost. In general, more expensive printers are used for higher-resolution color printing. A person whose job or business is commercial printing. A machine for printing text or pictures, especially one linked to a computer.

History:
The history of computer printers began in 1938 when Seattle inventor Chester Carlson (1906-1968) invented a dry printed process called electrophotography- commonly called a Xerox- which was to be the foundation technology for decades of laser printers to co me.

Working:
In short, printers work by converting digital images and text into physical copies. They do this using a driver or specialized software that has been designed to convert the file into a language that the printer can understand. The image or text is then recreated on to the page using a series of miniscule dots.
Best Printers for 2019:
- Canon Pixma G6020 Mega Tank All-in- One Printer
- Canon Pixma TR8520 Wireless Home Office All-In-One Printer
- Epson Eco Tank ET-4760 All-In=One Printer
- Epson Expression Photo HD XP-15000 Wide-Format Inkjet Printer
- HP LaserJet Pro M15w
- HP Sprocket 2nd Edition
- HP Tango X.
Types:
Printers are type of computer peripheral device that fall into two broad categories:
- 2D printers that print text and graphics onto paper
- 3D printers that create physical objects.
Advantages:
- Convenience- One of the main advantages of the printer is that it is convenient.
- Secure delivery- The Paper record can be easily anonymously delivered.
- Ease of reading- For most of the people, printed document will be easier read, as the text will be sharper.
Producing printed output:
In computing, a printer is a peripheral device which makes a persistent representation of graphics or text on paper.

The first computer was designed by Charles Babbage in the 19th century. Chester Carlson invented a dry printing process called electrophotography in 1938. The first electronic printer was the EP-101 which is invented by Japanese company Epson in 1968. The IBM 3800 printing system was the first high speed printer. It was the first laser printer which combine laser technology with electrophotography. After that, the inkjet printer was invented in 1976 and later Hewlett- Packard released Deskjet inkjet printer in 1992 which is 600 by 600 dots per inch resolution laser printer.
Printer:
A printer is a device that takes text and graphic output from a computer and transfer the information to paper.
Qualities of a Printer:
A printer has four qualities which are:
- Color
- Resolution
- Speed
- Memory
Printer Languages:
Printer languages are commands from computer to the printers to tell the printer what will be the font size, graphics and what will be the color. There are two famous printer languages which are:
- Postscript
- Printer Command Language
Types of Printers:
Printer can be divided into two main groups which are impact printers and non-impact printers.
Impact printers:
Impact printer produces text and images when wire pins on print head strike the ink ribbon by physically contacting the paper.
Non-Impact Printer:
Non-impact printer produces text and graphics on paper without actually striking the paper. The most popular non-impact printers are inkjet printer, laser printer and photo printer.
Inkjet printer:
The most popular printer for home computer users is Inkjet printer. Inkjet printers developed in the late 1950s but it was able to produce decent digital images in 1970. These higher quality inkjet printers were developed by different companies like Canon, Epson and Hewlett- Packard.

Uses of Inkjet Printer:
The basic uses of inkjet printers are to print copy of a document for school, print pictures on photo printer and print receipts for purchases made online.
Laser Printer:
The laser printer was firstly developed by Gary Stark weather in 1971. In this printer, laser technology is used to print images on the paper. In 1984, Hewlett-Packed introduced HP Laser Jet that is more affordable for a person. Laser printers are more complex than other printers.

Uses of Laser Printer:
The uses of laser printers are to do quickly print hundreds of pages and print hard copies of legal documents.
Photo Printer:
Photo printer is a printer which produces photo lab pictures. A photo printer is a color printer that can produce images that copy the color range and resolution of prints made from photographic film.

What is Laser Printer?
Laser printer is an electrostatic digital printing process. It produces high quality texts and graphics by repeatedly passing a laser beam back and forth over a negatively charged cylinder called a drum to define differentially charged image. The drum selectively collects electrically charged powdered ink and transfer the image into the paper.

Definition of Laser Printer:
A laser printer is a printer that uses a focused light to transfer text and images onto paper. The laser does not burn images onto the paper.
How it Operates?
In a laser print operation, a laser beam fires on a mechanical cylinder known as a photoreceptor. This results in a pattern on the photoreceptor that gets coated with toner. Because of electric charges, the tone sticks to the paper. Finally, the paper is heated in order to focus the toner to the paper.
History of Laser Printer:
The first laser printer was designed by Gary Stark weather in 1969. The original laser printer was known as EARS, which later became the Xerox. The first commercial laser printer was released by IBM company in 1976. Similarly, Japanese company Canon created world’s first desktop laser printer in 1979. The Xerox made first office use laser printer in 1981. In 2000, Xerox introduced solid ink printing for office and home printing supplies.
Multifunction peripheral (MFP)
A multifunction peripheral (MFP) is a device that performs a variety of functions that would otherwise be carried out by separate peripheral devices. As a rule, a multifunction peripheral includes at least two of the following:
• A printer
• A scanner
• A copier
• A fax machine
Multifunction peripheral devices often have a base function with one or more added capabilities. Here are some common examples:
• Digital copy machine: Creates copies digitally, by scanning and printing. In addition to scanning and printing, may include fax, sorter and office hardware, such as a stapler.
• Fax machine MFP: Looks like a normal fax but connects to a PC for data input/output, printing, scanning and copying.
• Printer/Scanner/Copier MFP: Performs all three functions and sometimes faxing as well.
Cost savings and lower space requirements make multifunctional peripherals a practical choice for many people who would ordinarily have to buy separate devices. On the other hand, those who require high-end functioning may be better served by a device dedicated to that particular use.
A thermal printer may refer to any of the following:

1. A thermal impact printer or electro thermal printer is a printer that uses heated pins to “burn” images onto heat-sensitive paper. These printers are commonly used in calculators and fax machines; and although they are inexpensive and print relatively fast, they produce low resolution print jobs.
2. A thermal printer, thermal transfer printer, or thermal wax-transfer printer uses thermal wax ribbon to melt colored wax on paper for a photo print. It was invented by Jack Kilby.
Mobile Printer:
Mobile printing is the process of sending wirelessly of sending data to a printer wirelessly from a smart-phone. It is smaller than its predecessor printers.

Benefits of Mobile Printer:
There are three important benefits of mobile printer. Firstly, it can be used anywhere. Secondly, it can be printed any size of paper. Thirdly, it can be connected to any device.
Label printer:
A label printer is a computer printer that prints on self-adhesive label material and/or card-stock (tags). A label printer with built-in keyboard and display for stand-alone use (not connected to a separate computer) is often called a label maker. Label printers are different from ordinary printers because they need to have special feed mechanisms to handle rolled stock, or tear sheet (fanfold) stock. Common connectivity for label printers include RS-232 serial, Universal Serial Bus (USB), parallel, Ethernet and various kinds of wireless. Label printers have a wide variety of applications, including supply chain management, retail price marking, packaging labels, blood and laboratory specimen marking, and fixed assets management.
Label printer uses:
Label printers use a wide range of label materials, including paper and synthetic polymer (“plastic”) materials. Several types of print mechanisms are also used, including laser and impact, but thermal printer mechanisms are probably the most common. There are two common types of thermal printer.
Direct thermal printers use heat sensitive paper (similar to thermal fax paper). Direct thermal labels tend to fade over time (typically 6 to 12 months); if exposed to heat, direct sunlight or chemical vapors, the life is shortened. Therefore, direct thermal labels are primarily used for short duration applications, such as shipping labels.
On the other hand, thermal transfer printers use heat to transfer ink from ribbon onto the label for a permanent print. Some thermal transfer printers are also capable of direct thermal printing. Using a PVC vinyl can increase the longevity of the label life as seen in pipe markers and industrial safety labels found in much of the market place today. There are three grades of ribbon for use with thermal transfer printers. Wax is the most popular with some smudge resistance, and is suitable for matte and semi-gloss paper labels. Wax/resin is smudge resistant, suitable for semi-gloss paper and some synthetic labels. Resin alone is scratch and chemical resistant, suitable for coated synthetic labels. When printing on continuous label stock, there is a tendency for the print location to shift slightly from label to label. To ensure registration of the print area with the target media, many label printers use a sensor that detects a gap, notch, line or perforation between labels. This allows the printer to adjust the intake of label stock so that the print aligns correctly with the media.

Types of label printer:
Label printer capabilities vary between home, corporate and industrial-oriented models.
Desktop label printers are usually designed for light to medium-duty use with a roll of stock up to 4″ wide. They are quiet and inexpensive.
Commercial label printers can typically hold a larger roll of stock (up to 8″ wide) and are geared for medium-volume printing.
Industrial label printers are designed for heavy-duty, continuous operation in warehouses, distribution centers and factories. Additionally, industrial portable label printers are designed for heavy-duty operation on location. They are usually handheld and come with an industrial hard case. Examples of applications are labeling for electrical installations, construction sites, and production floors where there are no computers.
RFID readers are specialized label printers that print and encode at the same time on RFID transponders (tags) enclosed in paper or printable synthetic materials. RFID tags need to have printed information for backwards compatibility with barcode systems, so human users can identify the tag.
Label printer applicators are designed to automate the labeling process. These systems are common in manufacturing and warehousing facilities that require cases and pallets to be labeled for shipping.
Labelling software runs on a general-purpose personal computer, and is designed to create and/or format labels for printing. The software can use native OS printer drivers, or embed drivers in the software, bypassing the OS print subsystem. It may work with dedicated label printers as described in this article, or use sheet- or continuous-fed labels in a general-purpose computer printer.

An electronic label maker, depicting buttons, LCD screen, and sample thermal label.
Personal label printers or label makers are handheld or small desktop devices. They are intended for home office and small business use. The cost of these printers is generally very low, making them popular with low volume users; but they print on special tapes, often thermal, which are usually expensive.
In the past, mechanical systems which worked by embossing a colored plastic tape, called embossing tape, were common. A hammer in the shape of the letter caused a letter-shaped extrusion on the opposite side of the tape. The raised plastic would discolor, providing visual contrast.
Today, this type has been almost completely displaced by electronic thermal transfer devices with built-in keyboard and display, and an integrated cartridge containing the label material (and print ribbon, if used).
Plotter Printer
Computer plotters are a type of output device commonly used for computer-aided design applications, to output large vector designs such as architectural blueprints. By moving a pen mechanically, plotters draw line art onto the surface of the paper to reproduce vector graphics drawn on a computer. Although ideal for printing large line art graphics, plotters could not reproduce raster graphics, and the introduction of wide format inkjet and laser printers have rendered them largely obsolete.
How Plotters Work
There are two main types of plotters for printing: flatbed plotters and drum plotters. Flatbed plotters use a system where the paper is fixed, and the plotter moves a pen up and down, and left and right to draw the required marks on the paper. Drum plotters move the pen up and down, and the paper left and right by rotating the drum. This enables drum plotters to have a footprint smaller than the final paper size. Plotters can use more than one pen, allowing different colors to be drawn.
Using Plotters
Plotters work in conjunction with CAD software on the computer, to output line drawings for plans, blueprints and other technical drawings. Due to the mechanical actions involved in moving the pen, compared to other types of printers such as ink jet and laser printers, early plotters were slow to produce their output. Only a small number of pen plotters are still in use commercially, with many refurbished models available at low prices in online auctions.
3. SPEAKERS, HEADPHONES, AND EARBUDS
Speakers:

- A speaker is a term used to describe the user who is giving vocal commands to a software program.
- A computer speaker is an output hardware device that connects to a computer to generate sound. The signal used to produce the sound that comes from a computer speaker is created by the computer’s sound card.
- How do speakers work?
- Evolution of the computer speaker.
- Rating a speaker.
- Why do we need computer speakers?
- Related pages.
How do speakers work?
Speakers are made up of a cone, an iron coil, a magnet, and housing (case). When the speaker receives electrical input from a device, it sends the current through the causing it to move back and forth. This motion then vibrates the outer cone, generating sound waves picked up by our ears.
Evolution of the computer speaker
When computers were initially released, they had onboard speakers built into the chassis that generated a series of different tones and beeps. The first internal computer speaker was invented by IBM in 1981 and produced basic, low quality sound. As technology progressed, onboard speakers moved to being built into the computer monitor and acquired the ability to produce voices, music, and other sound effects. The speakers were usually located on the bottom-left and bottom-right on the front of the monitor, but sometimes they were built into the left and right side of the monitor. When computer gaming, digital music, and other media became popular, manufacturers began to make external speakers that produced higher quality sounds and improved bass. The first external computer speaker was invented by Abinawan Puracchidas in 1991 and are still the dominant type of speaker for computers.
Rating a speaker
Speakers are rated in frequency response, total harmonic distortion, and watts.
The Frequency response is the rate of measurement of the highs and lows of the sounds the speaker produces.
THD (total harmonic distortion) is the amount of distortion created by amplifying the signal.
The Watts is the amount of amplification available for the speakers.
Why do we need computer speakers?
External speakers are connected to a computer or another device to give the sound more amplification (make it louder), add more bass with a subwoofer, or create surround sound. If you have a laptop, smartphone, or another device with built-in speakers, you do not need external speakers unless you need louder sounds, more bass, or surround sound.
HeadPhones:
Sometimes referred to as earphones, headphones are a hardware output device that either plug into a computer line out or speakers. Headphones allow you to listen to audio or watch a movie without disturbing people around you. The picture is an example of a USB headset from Logitech, which also include a microphone (an input device), a popular solution for computer gaming.

The first pair of audio headphones were invented by Nathaniel Baldwin in 1910. The U.S. Navy ordered 100 pairs them because they recognized the potential advantages, despite many people being skeptical about their usefulness. Headphones come in several shapes and styles. The traditional style looks similar to those shown above. Headphones utilize styrofoam or another soft fabric around the earpieces to provide a comfortable fit around your ear and a plastic or light metal band between each earpiece.

The most basic type of headphones, earbuds, are small and fit inside your ear. They are usually shaped in a specific way to be as comfortable as possible. Some earbuds come with several sets of different rubber inserts. Depending on the size of the user’s ears, they can choose the size of rubber insert that best fits their ear canal.
4. OTHER OUTPUT DEVICES
i. Data Projectors
ii. Interactive Whiteboards
iii. Force-Feedback Game Controllers and Tactile Output
Define projector data
A projector is an optical device used to project images, videos, presentations, or texts in any surface. There are so many ways to use a projector, however, we have to be aware that there are different.
Types of projectors used for different purposes.
1 FOCUS ring
2 ZOOM ring
3 Control panel
4 Air inlet grille
5 Air inlet grille
6 Air outlet grille
7 Terminal board
8 Speaker
9 Adjustment feet (front)
10 Adjustment feet (rear)
11 Lock bar
12 Foot Adjustme
13 Lamp cover
Caution: Do not replace the lamp immediately after using the projector because the lamp would be extremely hot and it may cause burns.
1 Power button
2 AUTO POSITION / S button
3 COMPUTER / W button
4 MENU button
5 STATUS indicator
6 POWER indicator
7 KEYSTONE/ENTER button
8 VIDEO/ X button
9 T button
Important: While the menu or the screen for the keystone adjustment or password entry is being displayed, the COMPUTER, VIDEO, and AUTO POSITION buttons function as the W, X, and S buttons respectively. • While the menu is on the screen, the KEYSTONE button functions as the ENTER button.
1 Power jack
2 COMPUTER IN terminal (1, 2) (Mini D-SUB 15-pin)
3 MONITOR OUT terminal (Mini D-SUB 15-pin)
4 Remote control sensor (Rear)
5 USB (COMPUTER) terminal
6 AUDIO IN terminal (Mini jack)
7 AUDIO OUT terminal (Mini jack)
8 S-VIDEO terminal
9 VIDEO terminal
10 Lock bar
11 SERIAL (RS-232C) terminal (D-SUB 9-pin)
12 AUDIO L/R terminals 13 Kensington Lock
Kensington Lock
This projector has a Kensington Security Standard connector for use with Kensington MicroSaver Security System. Refer to the information that came with the Kensington System for instructions on how to use it to secure the projector. Please contact Kensington Technology Group below.
1 ON button 2 MAGNIFY button 3 VOLUME UP, DOWN buttons 4 KEYSTONE button 5 MENU button 6 ENTER button 7 AV (Audio/Video) MUTE button 8 OFF button 9 ASPECT button 10 PAGE UP, DOWN buttons 11 AUTO POSITION button 12 Direction buttons 13 FREEZE button 14 VIDEO, S-VIDEO buttons 15 COMPUTER (1, 2) buttons
The UP and DOWN buttons are used in the KEYSTONE adjustment in addition to the volume control.
What is interactive white board?
An interactive whiteboard, also known as a smartboard, is an interactive display in the format of a whiteboard that reacts to user input either directly or through other devices. Interactive whiteboards are a billion dollar industry and are used in classrooms, boardrooms, engineering, coaching and the strategic planning of many types of projects.
Kinds of interactive white board:
Pen-based, infrared boards
Pen-based, electro-magnetic boards
Touch-based, mesh board
Touch based infrared board
Pen-based, infrared boards
These boards are usually the cheapest boards on the market. They work by sticking a special dongle onto an existing whiteboard and use a battery-operated pen to work. They come under a wealth of names, models and prices:E Beam, Mimio, Rainbow, VosaBoard, CleverBoard 3, 3M and Inter write Board.

Pen-based,electro-magnetic boards
These boards use a mesh of copper wires on the board to get their input. This means they don’t need a battery-operated pen, which saves on buying batteries. However, these boards do not double-up as normal dry-wipe boards. They are also usually more expensive than the boards above. Promethean, Clasus and IMEX are examples of this type of board.

Touch-based, mesh board:
This type of board allows the user to interact with their finger as well as a pen. Some of them allow you to use dry wipe markers on them too. They’re also reasonably priced. Examples include: Teamboard, Traceboard, Smartboard and IQBoard.

Touch based infrared board:
These boards have all the features of the above type board but just use a different technology. A lot of these boards are also magnetic, which is useful. Again dry wipe markers can be used on these. Examples include: Hitachi Starboard, TouchIT, GeneeBoard, InTech Board, Imex Dual board and Clever board Dual. These boards are usually cheap and are increasingly becoming very popular.
